Wednesday 14th December 2016, 10:00am
New insights into infectious brain conditions help to explain why some people – and animals – are more at risk than others.
A study in mice reveals how prion diseases - which include variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) in people and bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) in cows - can infect the gut if contaminated meat has been eaten.
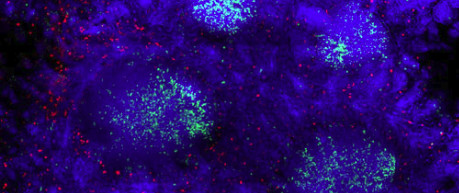
M cells are found in the lining of the gut and are part of the body's defences against infections. These specialised cells play a key role in transporting material across the lining of the gut where other cells of the immune system are waiting to repond.
A team – led by Professor Neil Mabbott at the University of Edinburgh’s Roslin Institute – found that prions use M cells to enable them to infect the gut. Mice that do not have M cells are completely resistant to prion infections. However, those that have a greater number of M cells in the lining of their gut, were around ten times more susceptible.
The findings may in part explain why most human cases have affected young people, who tend to have higher numbers of M cells in their guts than older people. The research also suggests that the presence of other infections in the gut such as Salmonella may increase the chances of prions causing infection.
Prion diseases - also known as transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs) – are infectious brain conditions that affect people and animals. They are caused by abnormally shaped proteins which can be passed on by eating contaminated meat. Prion diseases include vCJD in people, BSE in cows, scrapie in sheep and chronic wasting disease in deer. They cause extensive nerve and severe neurological symptoms including memory impairment, personality changes and difficulties with movement.
“Our next step is to understand how the prions exploit these cells to infect the gut. If we can design treatments to block the uptake of prions by M cells, this may provide a novel method to prevent prion infections in humans and animals.”
Professor Neil Mabbott, The Roslin Institute, University of EdinburghThe research is published in the journal PLOS Pathogens.
The Roslin Institute receives strategic funding from the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council.